Tooling Cost
Tooling cost appears as Hard Tooling Cost in the cost taxonomy under Capital Costs.
Tooling cost depends on factors in the following areas:
Tool Life for Plastic Molding
The tooling model estimates the number of parts that can be produced with a given tool before it wears to the point that it needs to be replaced. Based on that estimate, the cost model determines the number of tools required to manufacture the production volume specified in the Production Scenario tab of the Cost Guide, and accounts for that number of tools in total hard tooling cost.
Tool-life estimation is based on part material, and adjusted for tool material and tool coating type, as follows:
4 To determine an unadjusted value for the number of shots that can be endured by a single tool, the cost model looks up this number by part material in the lookup table tblToolLife.
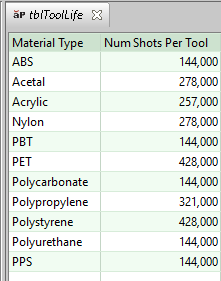
5 This value is then multiplied by the number of mold cavities (see Number and Layout of Mold Cavities), yielding the unadjusted number of parts that can be produced by a single mold.
6 The result is then adjusted for mold material by multiplying it by the tool shop property Tool Life Factor for the current mold material (see the setup option Mold Material in User Inputs for Plastic Molding).
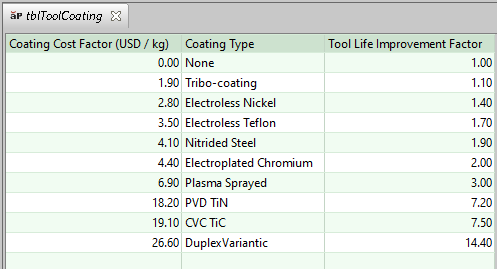
7 That result is then adjusted for mold coating by multiplying it by the Tool Life Improvement Factor looked up lookup in the table tblToolCoating by coating type (see the setup option Plating of the Mold in User Inputs for Plastic Molding).
For a given costing, either the formula Dependencies or Investment tab displays the number of tools assumed by tooling cost calculations.
Tooling-relevant Part GCDs
Tooling costs are affected by the following information obtained from GCD extraction:
• Number of simple holes considered Sleeve Pins (that is, simple holes for which the property sleevePinHole is true)
• Number of surfaces
• Number of small, medium, or large grill inserts (set by comparing GCD child artifacts for which the property isGrill is true, to established area size constraints)
• Number of ribs (set by the property isRib)
Mold Material Costs
Following are material costs whose values are specified in toolshop:
• Core and cavity plate material type and rate
• Ejector box material type and rate
• Actions material type and rate
• EDM carbon
SFM and RIM use less expensive mold material, by default, than IM.
Note: Core and cavity plate material costs are 0 with a standard (as opposed to custom) mold base. By default in starting point VPEs, a standard mold base is used—see the setup option Mold Construction Method in User Inputs for Plastic Molding.
Purchased Mold Component Costs
The following are among the plant variables whose values specify costs of purchased mold components:
• leaderPinsShoulderBushings
• returnPinsShoulderBushings
• ejectorGuidePinsBushings
• locatingRings
• sprueBushing
• stopPins
• sideLocks
• socketHeadCapScrewsShort
• socketHeadCapScrewsLong
• supportPillars
• sleevePins
• limitSwitches
• ejectorPins
• waterManifolds
• waterManifoldFittings
• waterHoses
• quickHoseDisconnects
• waterBaffles
Tooling Labor Costs
Labor rates for the following are specified in toolshop:
• Machining:
o CNC machining time and EDM machining time per cavity/core, die block, and action/cam, etc.
o Deep hole or gun drilling time for water cooling lines
• Assembly
• Design:
o 3D CAD modeling, mold flow, etc.
o NC programming time per cavity/core, die blocks, actions/cams, etc.
• Finishing/polishing
• Spotting
• Tryout
• CMM inspection
CNC Machining Versus EDM Burning
Some mold components are created with CNC machining only, some mold components are created with EDM burning only, and some mold components are created with a combination of CNC machining and EDM burning.
The cost model assumes the following:
• Only CNC machining is used to create the following components:
o Mold cavity
o Mold core
• Only EDM Burning is used to create sleeve pins.
• Both CNC machining and EDM burning are used to create the following components:
o Speaker grill inserts
o Rib inserts & insert pockets
o Lifters & lifter pockets
o Slides & slide pockets
Labor Costs for Mold Items Created with CNC Machining
Labor costs for CNC machining are based on CNC setup time and item machining time. Following are the mold items created by CNC machining, together with the factors that contribute to machining time:
Cavity & core machining time is the sum of the following
• Cavity & core volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
• Part surface area * time per unit area * number of cavities
• Runoff area * time per unit area
• Speaker grill volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
• Total insert volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
• Total insert pocket volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
Actions machining time is the sum of the following:
• Total lifter volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
• Total slide volume * time per unit volume * number of cavities
Labor Costs for Mold Items Created with EDM Burning
Labor costs for EDM burning are based on electrode design time as well as CNC setup and machining time for electrodes.
Electrode design depends on the number of the following features:
• Grill inserts
• Side cores
• Lifters
• Inserts (major, medium, minor)
CNC setup and machining time for the creation of electrodes is determined as follows:
• Setup time is 0.25 hours per electrode. The number of electrodes is the sum of the following:
o Total side cores * number of burns per side core
o Total lifters * number of burns per lifter
o Total major inserts * number of burns per major insert
o Total medium inserts * number of burns per medium insert
o Total minor inserts * number of burns per minor insert
o Total sleeve pins * number of burns per sleeve pin
o Total speaker grills * number of burns per speaker grill
• Machining time is 0.003 hours per electrode unit volume. The total electrode volume is determined as follows:
o Slide electrode volume * total side cores * number of burns per side core
o Lifter electrode volume * total lifters * number of burns per lifter
o Major insert electrode volume * total major inserts * number of burns per major insert
o Medium insert electrode volume * total medium inserts * number of burns per medium insert
o Minor insert electrode volume * total minor inserts * number of burns per minor insert
o Sleeve pin electrode volume * total sleeve pins * number of burns per sleeve pin
o Speaker grill electrode volume * total speaker grills * number of burns per speaker grill
This part of the cost model assumes a maximum of 4 side cores. It also assumes the following regarding the number of burns per feature:
• Side cores: 3 burns each
• Lifters: 2 burns each
• Major inserts: 4 burns each
• Medium inserts: 3 burns each
• Minor inserts: 2 burns each
• Sleeve pins: 2 burns each
• Speaker grills: 3 burns each
Miscellaneous Tooling Costs
Costs for the following also affect tooling costs:
• Heat treatment (rate specified in toolshop. Multiplied by sum of weights for core plates, cavity plates, inserts, and actions.)
• Plating (default plant variable for nitride plating. Multipliers set for all other plating types)
• Stress relief (default rate specified in toolshop)
• Texture (default plant variable for coarse texture. Multipliers set for all other textures)
• Freight (default rate specified in toolshop)
• Markup/profit (default rate specified in toolshop)